Mucinous Cystadenocarcinoma of the Breast with Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis
An Entity with an Unusual Clinical Course
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21141/PJP2024.09Keywords:
mucinous cystadenocarcinoma, breast cancer, axillary lymph node metastasisAbstract
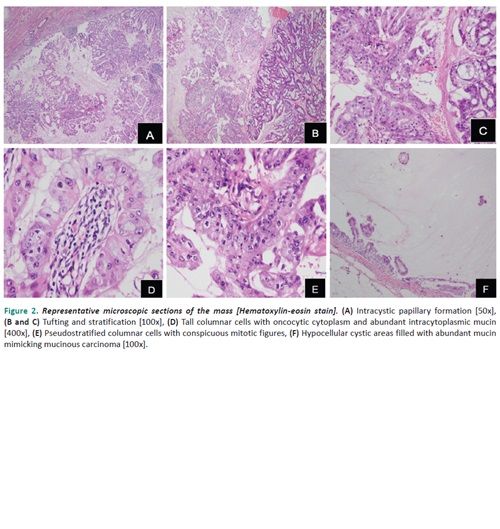
This is a case of a 54-year-old, perimenopausal, Asian, woman, who presented with an enlarging left breast mass associated with whitish to bloody nipple discharge. A core needle biopsy, done in another institution, showed histologic findings of a mucinous carcinoma with triple negative “basal-like” biomarker status (ER, PR, HER2/neu). Six cycles of neoadjuvant chemotherapy were given after which the subsequent modified radical mastectomy revealed a centrally located, 10.0 cm, well-circumscribed, nodular, ovoid mass on gross examination. Microscopic findings showed tall columnar cells in stratification, tufts and papillary formations, with surrounding abundant extracellular mucin. The individual tumor cells exhibit enlarged, hyperchromatic, basally located nuclei with prominent nucleoli, abundant amphophilic and occasionally oncocytic cytoplasm which contains intracytoplasmic mucin. Based on the histologic features, “basal-like” biomarker expression, and additional immunohistochemical studies (positive CK7, negative CK20 and CDX2), this case demonstrates a pure mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the breast. In addition to the rare histologic type, this case is exceptional since, despite multiple cycles of neoadjuvant chemotherapy, presence of extensive lymphovascular invasion and axillary lymph node involvement with extranodal extension remain evident.
Downloads
References
Kaur K, Shah A, Ghandi, J, Trivedi P. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2022;34:9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43046-022-00112-9.
Valdespino VE, Matamoros IL, Valle ML, Rangel MM, Ramon HM, Gomez VV. Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the breast, case report. Obstet Gynecol Rep. 2019;3:2-3. https://doi.org/10.15761/OGR.1000138. DOI: https://doi.org/10.15761/OGR.1000138
Koenig C, Tavassoli FA. Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the breast. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998; 22:698–703. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9630176. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000478-199806000-00006. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/00000478-199806000-00006
WHO classification of tumors of the breast. Lyon (France): International Agency for Research on Cancer.
Kazuhiro S, Tashiro T, Uraoka N, et al. Primary mammary mucinous cystadenocarcinoma: cytological and histological findings. diagnostic cytopathology. Diagn Cytopathol. 2012;40(7):624-8. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21472867. https://doi.org/10.1002/dc.21638. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/dc.21638
Moatasin A, Mamoon N. Primary breast mucinous cystadenocarcinoma and review of literature. Cureus. 2022;14(3):e23098. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35464581. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8997314. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.23098. DOI: https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.23098
Kamrani G. Nikbakhsh N, Hosseini A, Ghorbani H, Arefisigaroudi N, Davarian A. Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of breast in a 69-year-old woman with positive hormone receptors, the first case reported. Caspian J Intern Med. 2021: 12 (Suppl 2):S444-6. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34760102. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8559632. https://doi.org/10.22088/cjim.12.0.444.
Deng Y, Xue D, Wang X, et al. Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the breast with a basal-like immunophenotype. Pathol Int. 2012;62(6):429-32. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1827.2012.02810.x
Koufopoulos N, Goudeli C, Syrios J, Filopoulos E, Khaldi L. Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the breast: the challenge of diagnosing a rare entity. Rare Tumors. 2017;9(3):7016. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29081926. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5643878. https://doi.org/10.4081/rt.2017.7016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4081/rt.2017.7016
Nayak A, Bleiweiss IJ, Dumoff K, Bhuiya TA. Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the breast: report of 2 cases including one with long-term local recurrence. Int J Surg Pathol. 2018;26(8):749-57. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29745281. https://doi.org/10.1177/1066896918775810. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1066896918775810
Rakıcı S, Gönüllü G, Gürsel SB, Yıldız L, Bayrak IK, Yücel I. Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the breast with estrogen receptor expression: a case report and review of literature. Case Rep Oncol. 2009;2(3):210-6. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20737039. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2914384. https://doi.org/10.1159/000253866. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1159/000253866
Honma N, Sakamoto G, Ikenaga M, Kuroiwa K, Younes M, Takubo K. Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the breast: a case report and review of literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2003;127(8):1031-3. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12873181. https://doi.org/10.5858/2003-127-1031-MCOTBA. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5858/2003-127-1031-MCOTBA
Petersson F, Pang B, Thamboo TP, Putti TC. Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the breast with amplification of the HER2-gene confirmed by FISH: the first case reported. Hum Pathol. 2010;41(6):910-3. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20338619. 10.1016/j.humpath.2009.10.020.
Kaur K, Shah A, Gandhi J, Trivedi P. Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the breast: a new entity with broad differentials—a case report. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2022;34(1):9. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35224708. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43046-022-00112-9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43046-022-00112-9
Dabbs D. Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry: theranostic and genomic applications, 3rd ed. Philadelphia; 2010.
Vang R, Gown AM, Barry TS, et al. Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in primary and secondary mucinous tumors of the ovary: analysis of coordinate immunohistochemical expression profiles and staining distribution in 179 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006;30(9):1130-9. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16931958. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.pas.0000213281.43036.bb. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/01.pas.0000213281.43036.bb
Fukushima N, Fukayama M. Mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas: pathology and molecular genetics. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2007;14(3):238-42. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17520198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00534-006-1168-3. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00534-006-1168-3
Sessa F, Bonato M, Frigerio B, et al. Ductal cancers of the pancreas frequently express markers of gastrointestinal epithelial cells. Gastroenterology. 1990;98(6):1655-65. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1692551. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-5085(90)91104-e. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-5085(90)91104-E
Rokutan H, Hosoda F, Hama N, et al. Comprehensive mutation profiling of mucinous gastric carcinoma. J Pathol. 2016;240(2):137-48. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27313181. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.4761. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/path.4761
NCCN guidelines version 5: breast cancer. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast.pdf
Petersson F, Pang B, Thamboo TP, Putti TC. Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the breast with amplification of the HER2-gene confirmed by FISH: the first case reported. Hum Pathol. 2010;41(6):910-3. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20338619. https://doi.org/c10.1016/j.humpath.2009.10.020 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2009.10.020
Shimada M, Imura J, Kozaki T, et al. Detection of Her2/neu, c-MYC and ZNF217 gene amplification during breast cancer progression using fluorescence in situ hybridization. Oncol Rep. 2005;13(4):633-41. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15756435. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3892/or.13.4.633
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 PJP

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.








